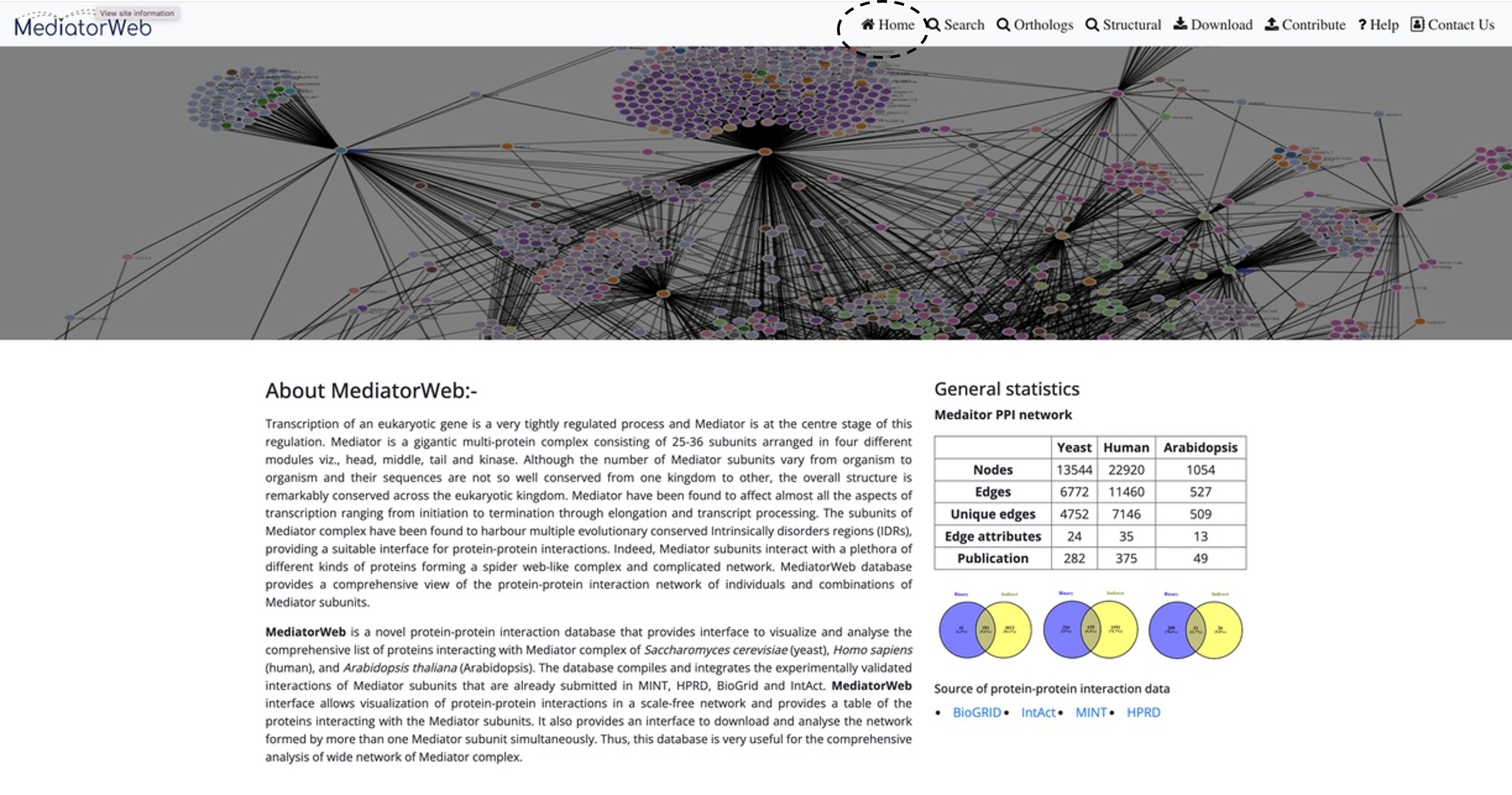
Home
MediatorWeb is a database and web interface to visualize the protein-protein interaction (PPI) network of Mediator complex of yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae), human (Homo sapiens) and Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana). We have complied the experimentally validated interaction data for Mediator subunits of these three model organisms from MINT, HPRD, IntAct and BioGRID databases and, catalogued them systematically for the researchers trying to explore the functions of Mediator complex. The portal of MediatorWeb comprises mainly four interfaces: i) Interaction query and result section, ii) Network Visualization and Interaction Table, iii) orthologs of proteins interacting with Mediator subunits and iv) Structural Information Interface. The home page displays the general statistics of the PPI (Protein-Protein Interaction) network of Mediator complex in human, yeast, and Arabidopsis. The list of interacting proteins in these organisms are further catalogued into direct and indirect interaction categories based on the type of methods used to study the interactions. Only those interactions, which have been validated experimentally in one-to-one interaction methods, are placed in ‘Direct’ and other physical interactions are categorized into “indirect” interactions.
Search
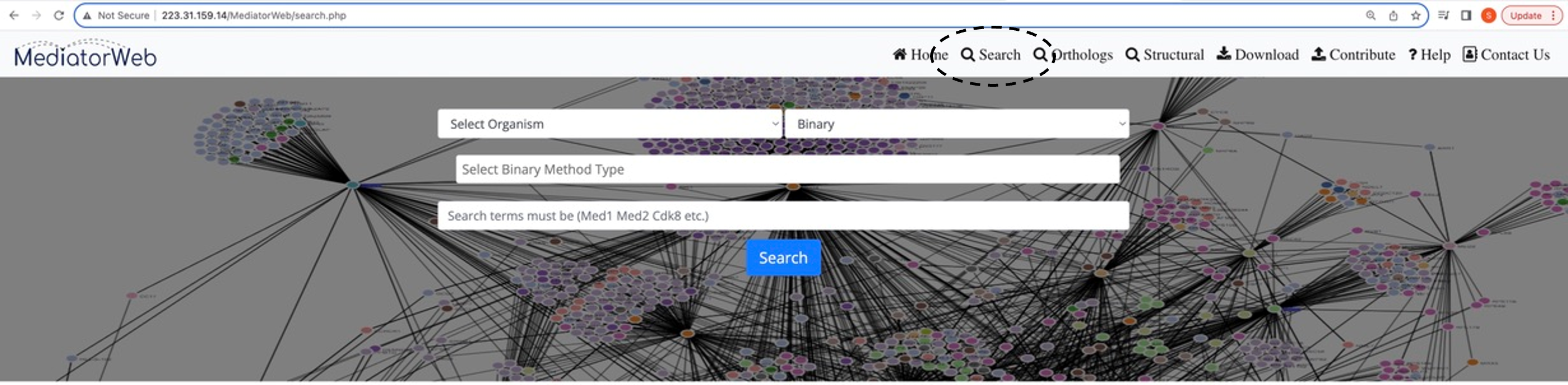
Query search
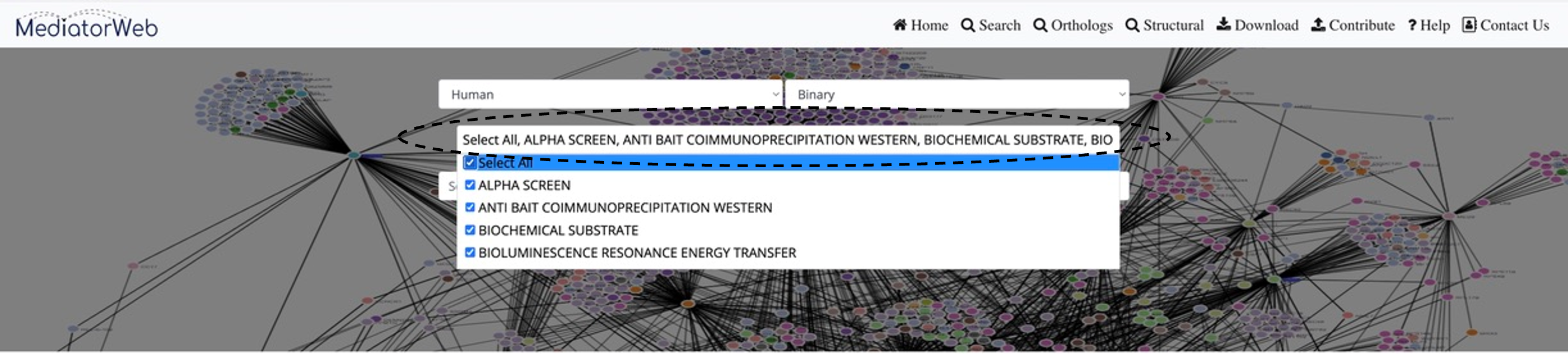
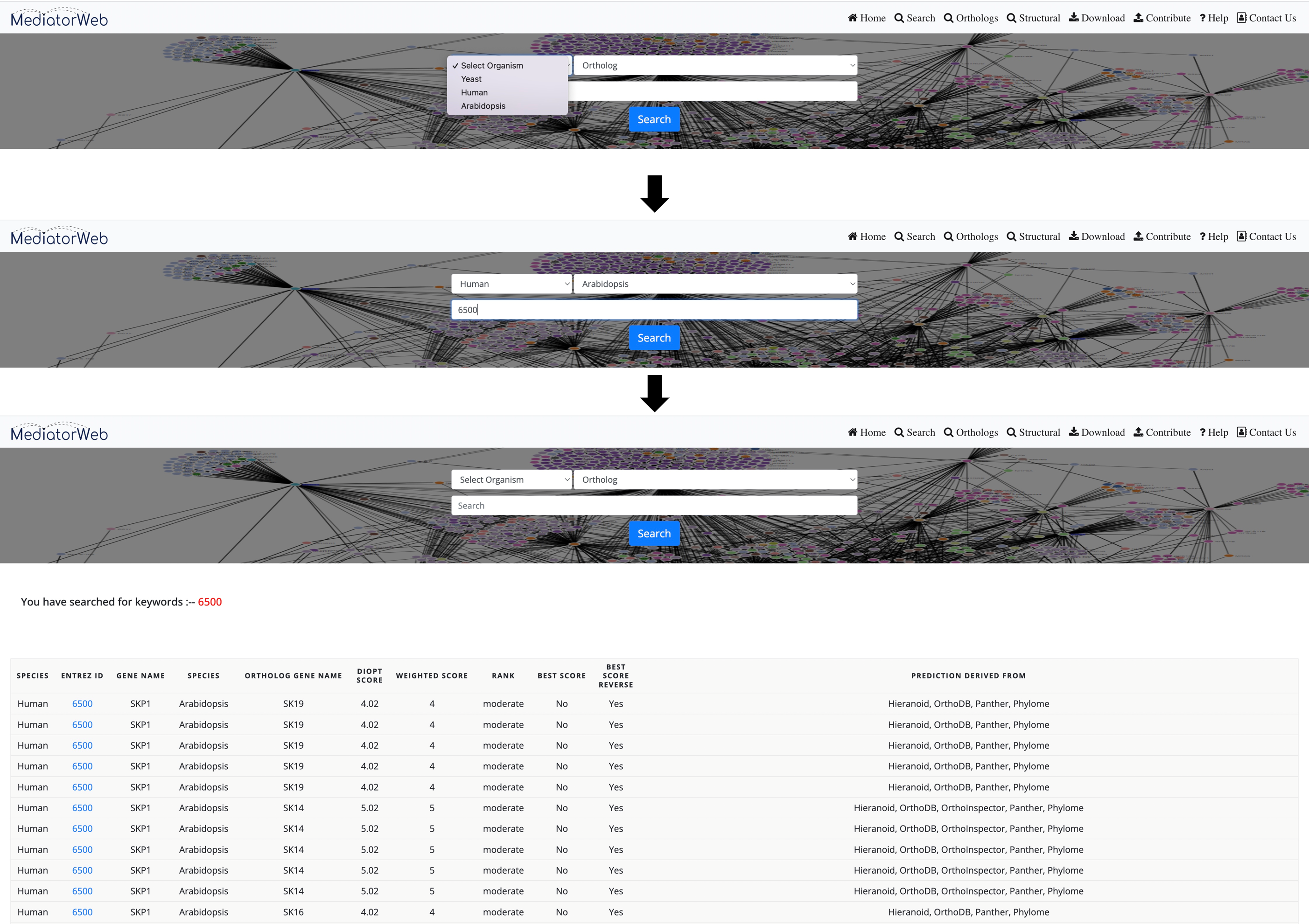
First, select the organism. The database contains entries from three model organisms: Yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae), Human (Homo sapiens), and Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana). After selecting the organism, the interface provides options for physical interactions. Physical interactions are further divided into two categories: direct (binary) and indirect interactions and can then choose from different Method Types. Users can select one or more Method Types for both direct and indirect interactions to extract the interactions from the database.

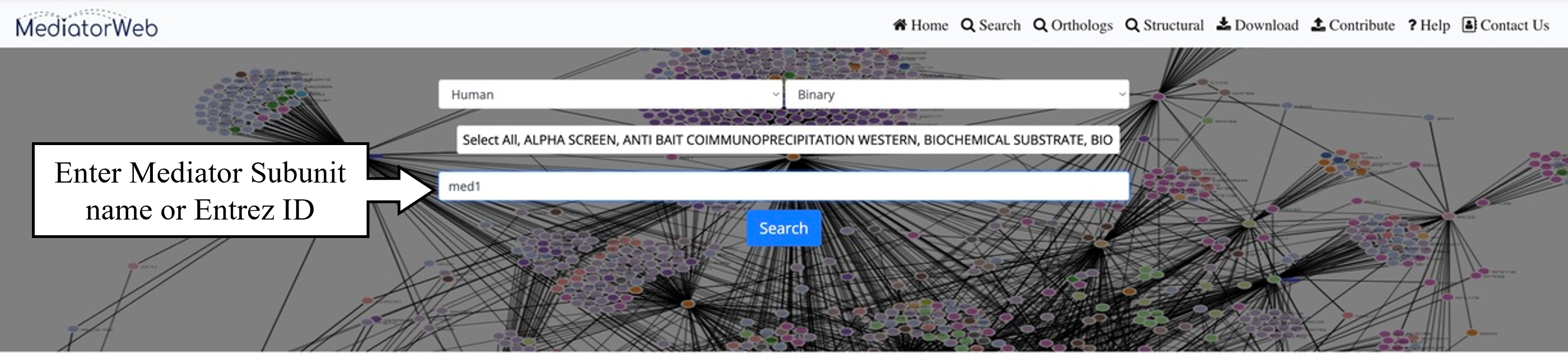
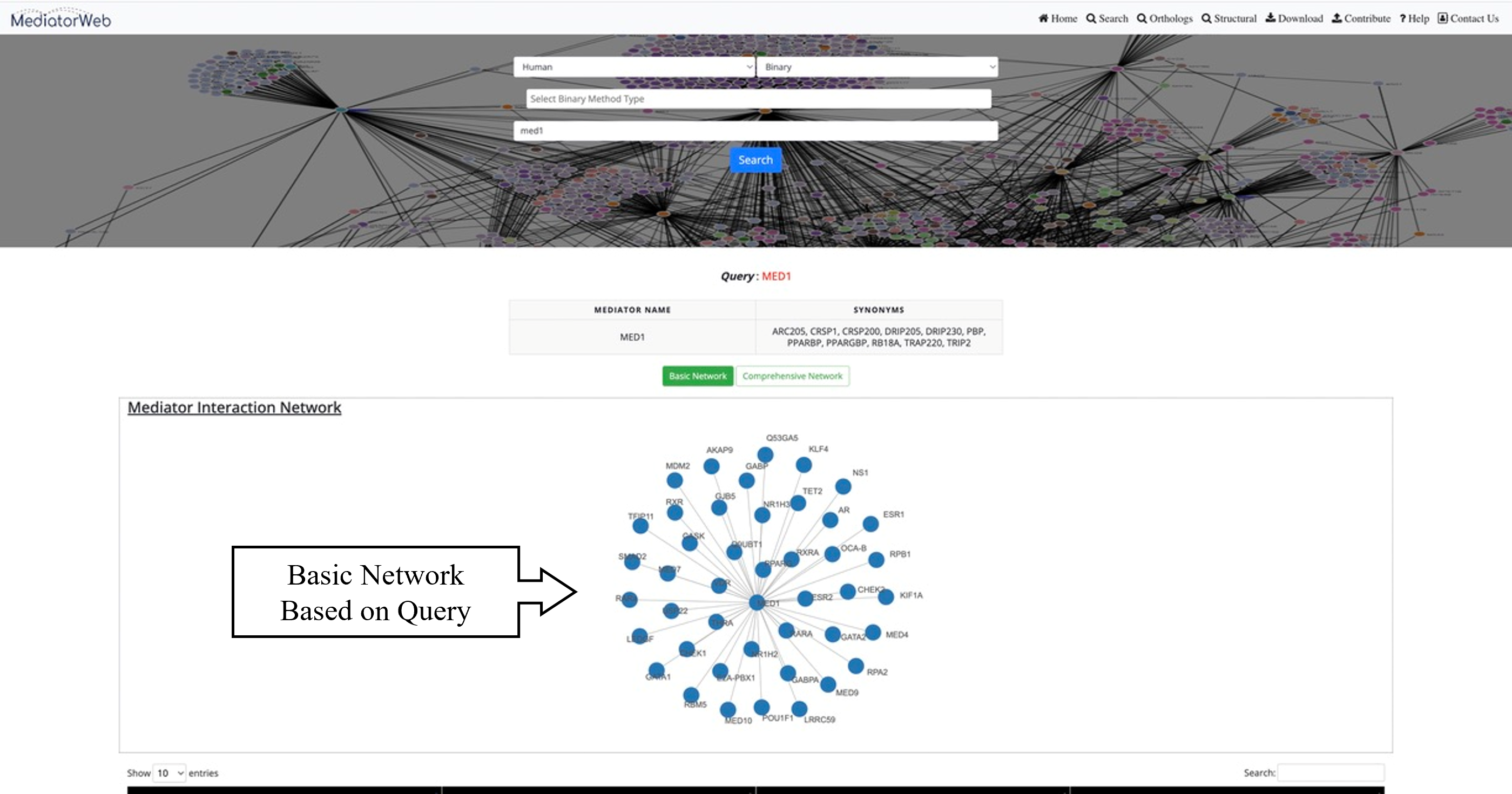
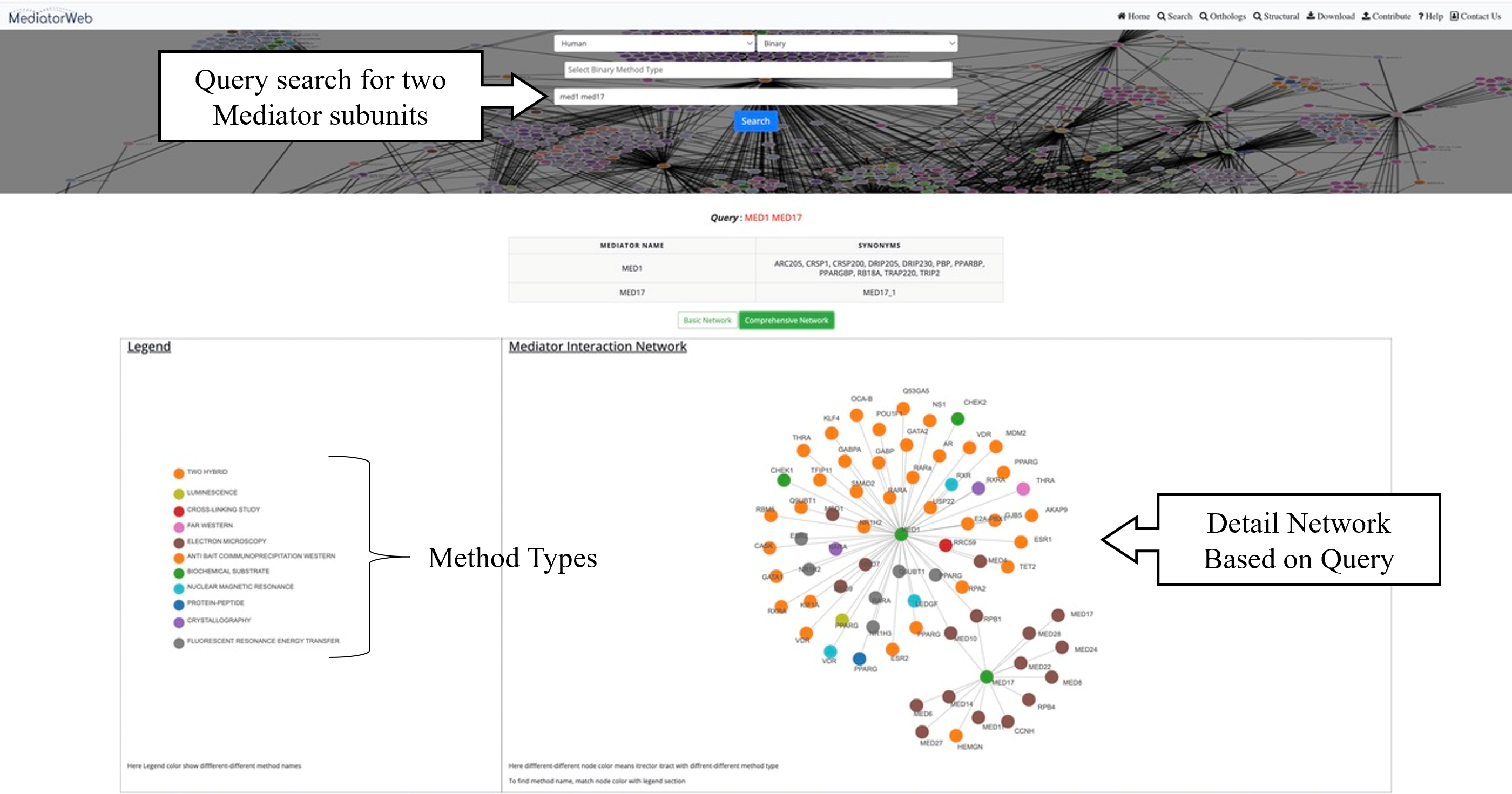
4) Search:The 'search tab' allows the user to input the name of a Mediator subunit in order to extract the PPI network associated with the selected Mediator subunit. In the current version of the MediatorWeb database, users can perform queries using either the Mediator gene symbol (as provided in the universal unified nomenclature of Mediator subunits) (Henri-Marc Bourbon et al., 2004; Nagulapalli et al., 2016) or the Entrez IDs of Mediator subunits. Users have the freedom to query for a single Mediator subunit or multiple Mediator subunits, as demonstrated in the example. The MediatorWeb interface processes the query input and provides a list of interacting proteins and the corresponding PPI network and table as output.
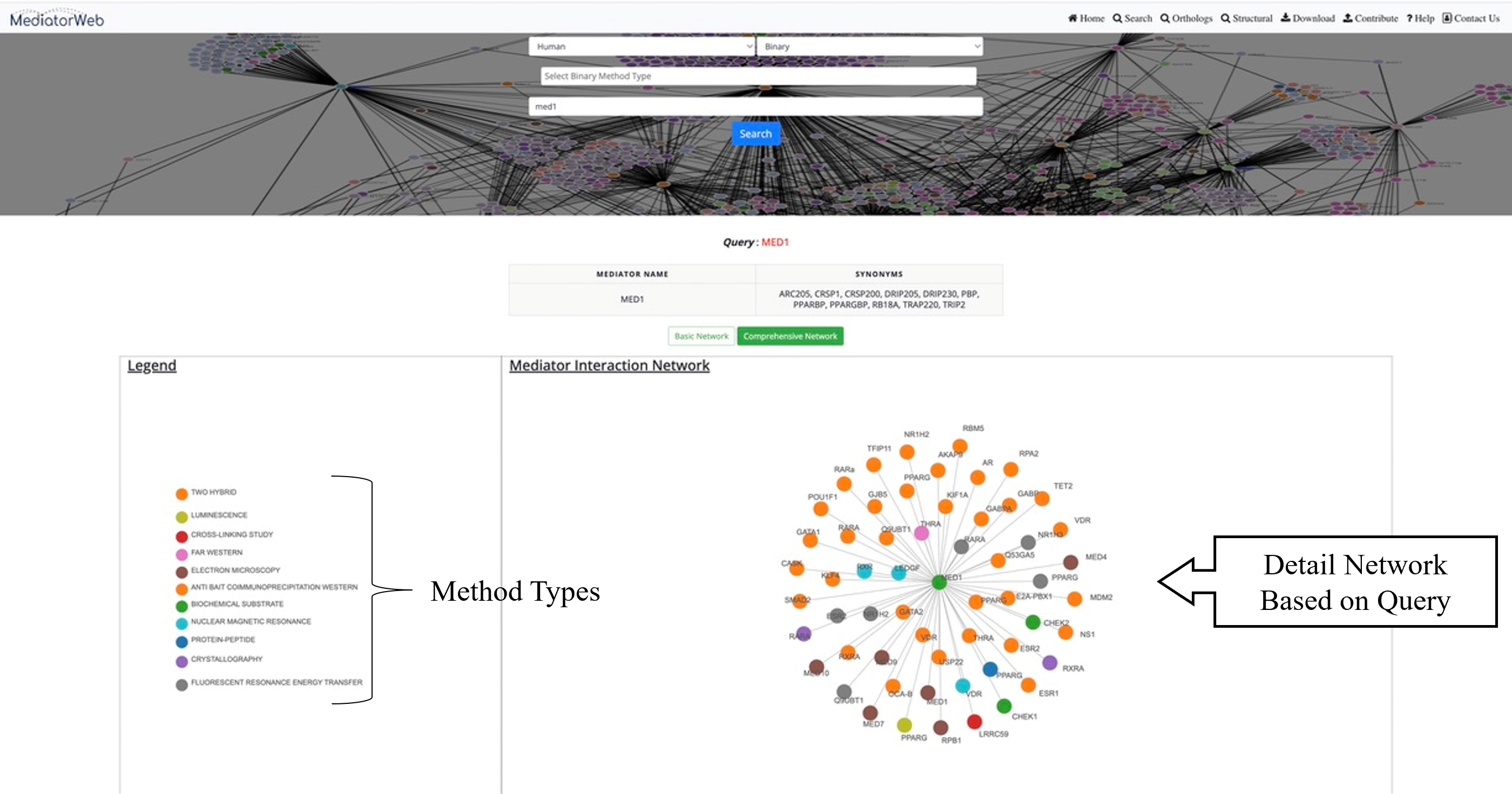
Network: MediatorWeb provided two types of networks to visualized and analysed the PPI of Mediator complex. i) Basic network: showing only the distinct edges. ii) Comprehensive network: providing the thorough depiction of the network, encompassing all edges along with the respective methods through which Mediator subunits interact with other proteins.
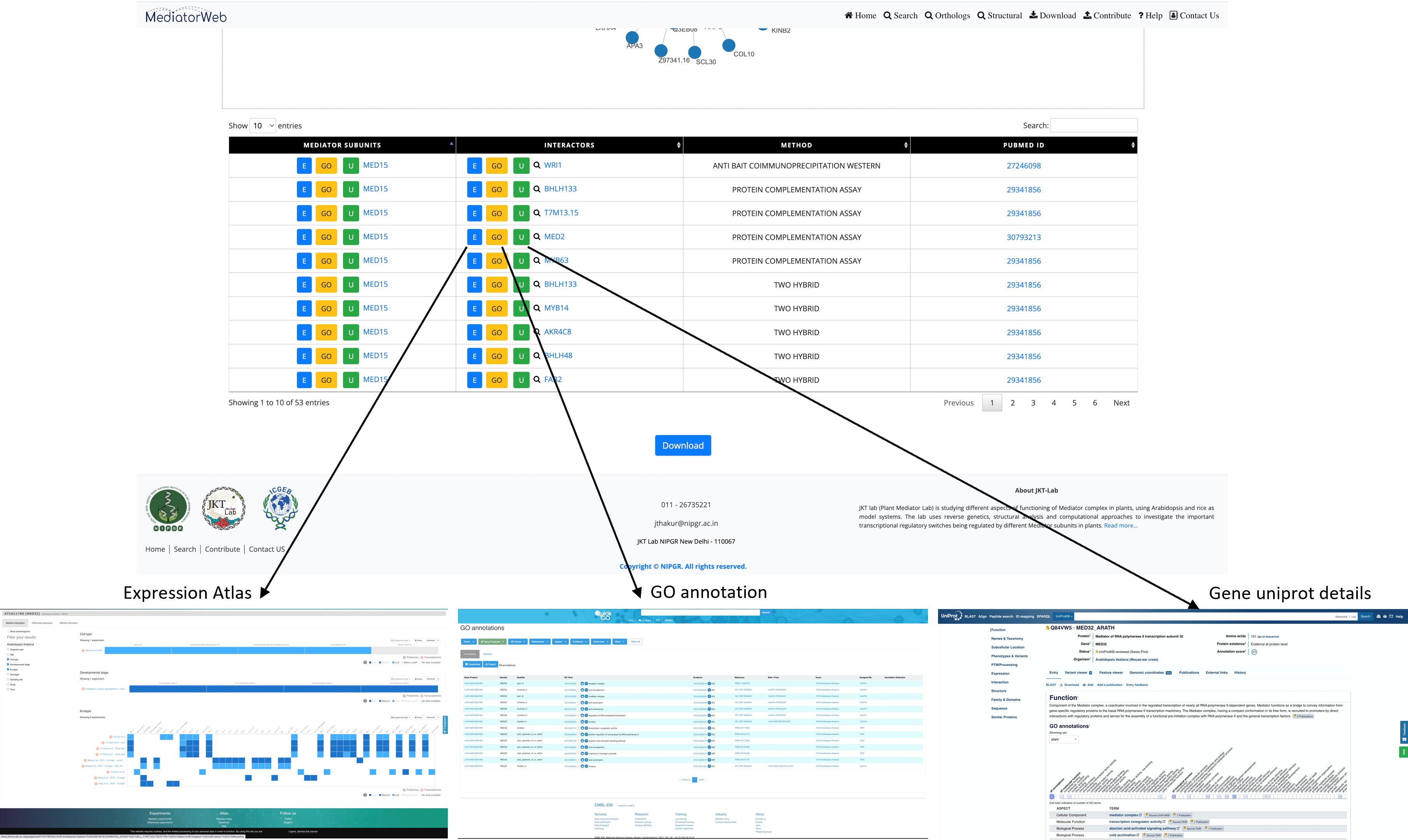
Result table: In addition to the network visualization feature, the MediatorWeb database offers users the ability to download a table containing information about interacting proteins. This table includes details such as the Mediator subunit, the symbol of the interacting protein, the method used to detect the interaction, and the PubMed ID of the reference article. Furthermore, all Mediator subunits and interacting proteins are hyperlinked to external portals that provide NCBI and UniProt gene information, as well as a link to the Expression Atlas webpage, which offers insights into expression patterns in various tissues and conditions for additional information. The PubMed IDs are also linked to the NCBI PubMed portal, allowing users to easily access related research articles by clicking on them in a new tab.
Orthologs
We used DIOPT (http://www.flyrnai.org/diopt) ortholog prediction tool to identify the orthologs of the proteins that has been found to interact with the Mediator complex. DIOPT is an ortholog finder integrating different ortholog prediction tools to provide a homology score for each predicted ortholog pair. The chosen tools provide a balance between sensitivity and specificity for the prediction of orthologs between the gene pair. These tools utilize phylogeny, sequence similarity and PPI based orthologs prediction. Therefore, DIOPT calculates a simple score based on the number of tools that support a given orthologous gene-pair relationship.
Download
User can download the complete list of interactions and tables used in the article.
Contribute
The MediatorWeb database has been designed to accommodate high quality contributions from researchers working with Mediator subunits. Such contributions to the database will be highly appreciated. We will be pleased to add any new data and updates related to PPI of the yeast, human and Arabidopsis Mediator complex. Users can contribute to the database in two ways, 1) Scientist and researcher are welcome to visit and submit the Mediator interaction protein to this database. Scientist can directly submit or send the list of interacting proteins in the prescribed excel format, which will be further edited and checked by the expert curators to screen each entry to the MediatorWeb. The list can be sent to jthakur@nipgr.ac.in. 2) While we are working hard to include all the interactors of Mediator complex. For the current version of MediatorWeb, we have taken information from MINT, HPRD, BioGrid and InAct databases and also from different publications. There is a possibility that we might have missed few interactions. So, if you find any interactions of Mediator subunits (of yeast, human and Arabidopsis) missing from MediatorWeb database, please feel free to let us know about it. You can always send an email to jthakur@nipgr.ac.in.